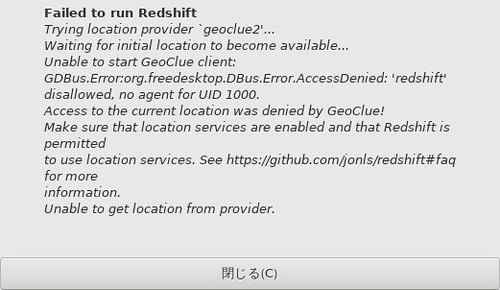
Nextcloud 15 がリリースされました.
14.0.4 からアップグレードしようとしましたが失敗しました.そのメモです.
$ sudo -u www-data php7.0 ./occ upgrade
Nextcloud or one of the apps require upgrade - only a limited number of commands are available
You may use your browser or the occ upgrade command to do the upgrade
Set log level to debug
Updating database schema
Updated database
UnexpectedValueException: The files of the app "user_external" were not correctly replaced before running the update
Update failed
Maintenance mode is kept active
Reset log level
整合性が保たれていないようなので手動でアーカイブを入手して比較すると同じに見える
$ wget https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/nextcloud-15.0.0.tar.bz2 https://download.nextcloud.com/server/releases/nextcloud-15.0.0.tar.bz2.asc
$ gpg --verify ./nextcloud-15.0.0.tar.bz2.asc
gpg: 署名されたデータが'./nextcloud-15.0.0.tar.bz2'にあると想定します
gpg: 2018年12月10日 19時27分11秒 JSTにRSA鍵ID A724937Aで施された署名
gpg: "Nextcloud Security <security@nextcloud.com>"からの正しい署名
gpg: *警告*: この鍵は信用できる署名で証明されていません!
gpg: この署名が所有者のものかどうかの検証手段がありません。
主鍵フィンガー・プリント: 2880 6A87 8AE4 23A2 8372 792E D758 99B9 A724 937A
$ tar tvf ./nextcloud-15.0.0.tar.bz2 | lv
$ tar xf ./nextcloud-15.0.0.tar.bz2
$ sudo -u www-data rsync -acvvn ./nextcloud/apps/user_external /var/www/home.matoken.org/nextcloud/apps/
sending incremental file list
delta-transmission disabled for local transfer or --whole-file
user_external/
user_external/appinfo/app.php is uptodate
user_external/appinfo/database.xml is uptodate
user_external/appinfo/info.xml is uptodate
user_external/appinfo/signature.json is uptodate
user_external/img/app.svg is uptodate
user_external/lib/base.php is uptodate
user_external/lib/ftp.php is uptodate
user_external/lib/imap.php is uptodate
user_external/lib/smb.php is uptodate
user_external/lib/webdavauth.php is uptodate
total: matches=0 hash_hits=0 false_alarms=0 data=0
sent 515 bytes received 587 bytes 2,204.00 bytes/sec
total size is 19,690 speedup is 17.87 (DRY RUN)
このあたりのバグぽい
- Upgrade from 14 to 15 Beta failed · Issue #12506 · nextcloud/server
- Nextcloud-15.0 & user_external-0.4 #68
ちなみに user_external はFTP, IMAP, SMB の認証周りのよう.
Authenticate user login against FTP, IMAP or SMB.
とりあえず該当の user_external を無効にしてアップグレードは通った
$ sudo -u www-data php7.0 ./occ app:disable user_external
$ sudo -u www-data php7.0 ./occ upgrade
通ったけど無効にしていても怒られる
Some files have not passed the integrity check. Further information on how to resolve this issue can be found in the documentation. (List of invalid files… / Rescan…)
Technical information
=====================
The following list covers which files have failed the integrity check. Please read
the previous linked documentation to learn more about the errors and how to fix
them.
Results
=======
- user_external
- EXTRA_FILE
- user_external/appinfo/signature.json
Raw output
==========
Array
(
[user_external] => Array
(
[EXTRA_FILE] => Array
(
[user_external/appinfo/signature.json] => Array
(
[expected] =>
[current] => 37efcee67605ab01a595df9b8e37a63f0260a8d795cb4af9b1b40e137ace928193747445954b22455fcbfd1758ea9b663153afc73438f5370725682e344c8723
)
)
)
)
まだ非対応アプリも多いしメイン環境は暫く待ったほうが良さそうな感じです.
環境
$ sudo -u www-data php7.0 ./occ status -v
- installed: true
- version: 15.0.0.10
- versionstring: 15.0.0
- edition:
$ lsb_release -d
Description: Ubuntu 16.04.5 LTS
$ uname -m
x86_64